1990’lardan bu yana, her yıl Bilkent Üniversitesi Elektrik ve Elektronik Mühendisliği (EEE) Bölümü ve IEEE Bilkent Öğrenci Kolu, Bilkent EEE lisansüstü ve seçilmiş lisans öğrencilerinin çalışmalarını bilgi paylaşımı festivali şeklinde sergiledikleri bir etkinlik olan Lisansüstü Araştırma Konferansı’nı (GRC) düzenlemektedir. Gün boyu süren etkinlik sırasında, Bilkent EEE lisansüstü öğrencileri son teknoloji araştırma projelerini etkileşimli sözlü ve poster sunumlarıyla anlatırken, seçilen lisans öğrencileri ders proje demolarını sunmaktadır.


Bu yılki GRC, 27 Ocak 2023 Cuma günü gerçekleştirilmiştir. Etkinlik, bilgi paylaşımıyla dolu bir gün ve lisans öğrencilerine Bilkent Üniversitesi EEE Bölümü’nde yürütülen mühendislik ve bilim araştırma dünyasını deneyimlemeleri için eşsiz bir fırsat sunmuştur.


Bu seneki program, 4 zaman bloğunun her birinde eş zamanlı olarak üç oturumun gerçekleştirildiği toplam 12 oturumda gruplandırılmış olan 48 sözlü sunum içermiştir. Sunumlarda, lisansüstü ve seçilen lisans öğrencileri özgün araştırma projelerini paylaşarak, dinleyicilerin sorularını yanıtlamıştır. Yapay zekâ ve makine öğrenmesi, sinyal işleme, iletişim ve ağ oluşturma, biyomedikal mühendisliği, elektronik, elektromanyetik, kontrol ve robotik, optik ve fotonik ve nanoteknoloji dahil olmak üzere elektrik ve elektronik mühendisliğinin çeşitli alanları ele alınmıştır. Konferansa, Bilkent EEE lisansüstü ve lisans öğrencilerinin de aralarında bulunduğu 200’den fazla katılımcı katılmıştır.


Konferans, bölüm tarafından en iyi 3 sunum ve 1 poster ödülünün verildiği ödül töreni ile sona ermiştir. Konferansın başkanlığını Doç. Dr. Muhammed Ömer Sayın yapmıştır. Etkinliğin organizasyonunda, lisansüstü öğrenciler Merve Begüm Terzi, Issifu Iddrisu ve Ahmet Safa Öztürk ile IEEE Bilkent Öğrenci Kolu’ndan lisans öğrencileri yer almıştır. GRC hakkında daha fazla bilgi https://ieee.bilkent.edu.tr/grc2023/index.html adresinde bulunabilir.
Konferansta ödül alan konuşmalar ise şöyle:
Sözlü Sunum Ödülleri:
- ResViT: Minimum Electric Field Gradient Array Body Coil with Adjustable Regions of Linearity
Reza Babaloo, Ergin Atalar
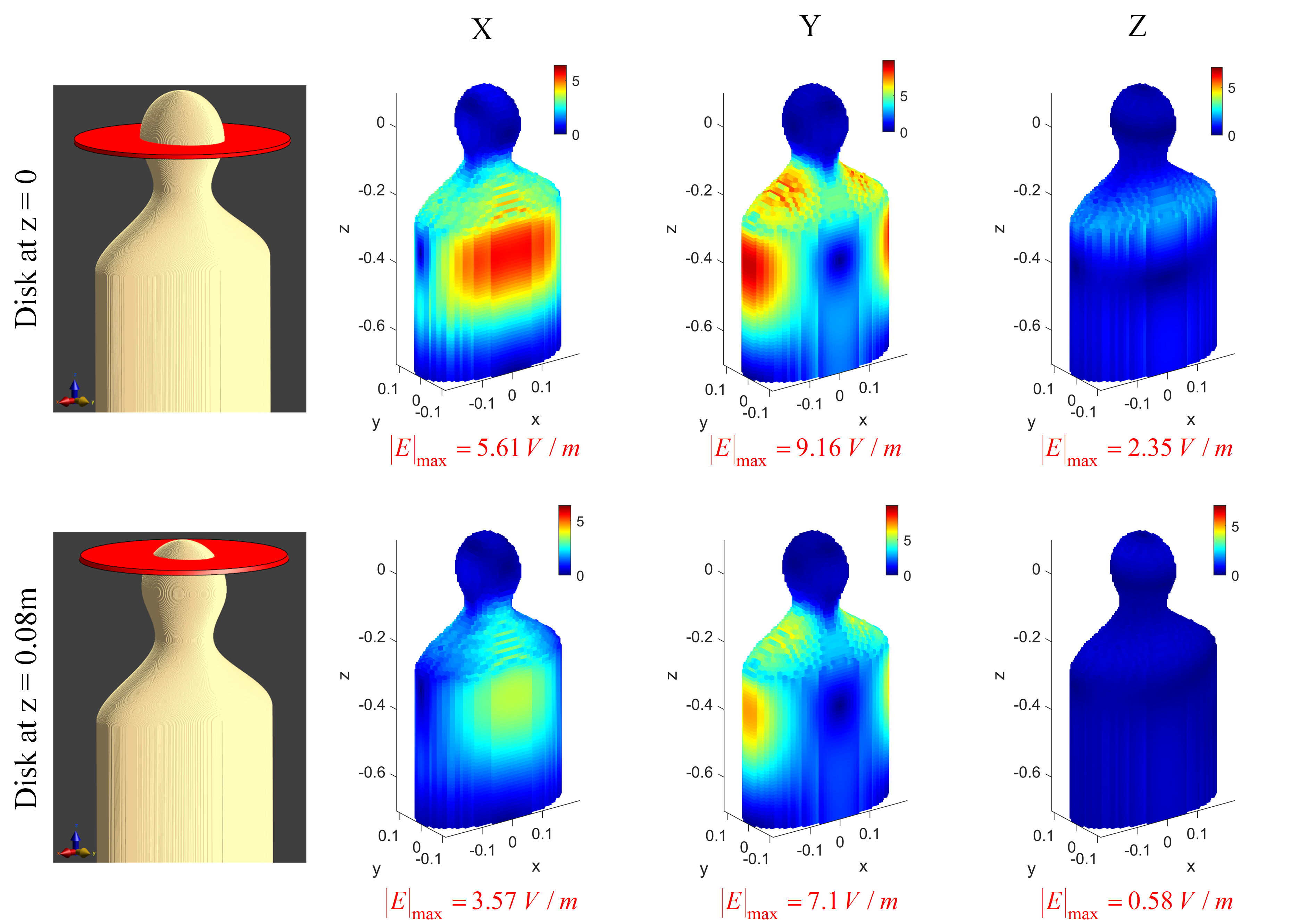
The rapid switching of magnetic fields (B-fields) induces electric fields (E-fields) within the human body, which causes peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS). A large region of linearity (ROL) in whole-body gradient coils exposes large body areas to switching magnetic fields, inducing high E-fields. However, a large ROL is not necessary for all MRI examinations. Several short-body and head-insert gradient coils with small ROL were developed to increase gradient strength without causing PNS. Recent gradient design algorithms incorporate constraints on the E-fields, leading to PNS-optimized gradient coils. Despite these efforts, further optimization cannot be performed after coil fabrication. A body gradient array coil (made up of multiple coil elements) can produce linear gradients in different ROL shapes by optimizing the feeding currents, which can alter the induced E-fields. This work shows the performance of the gradient array coil in minimizing E-field when the desired gradient is required in various ROL.
- An Absorbing Markov Chain-based Approach for the Distribution of Age of Information
Ege Orkun Gamgam, Nail Akar
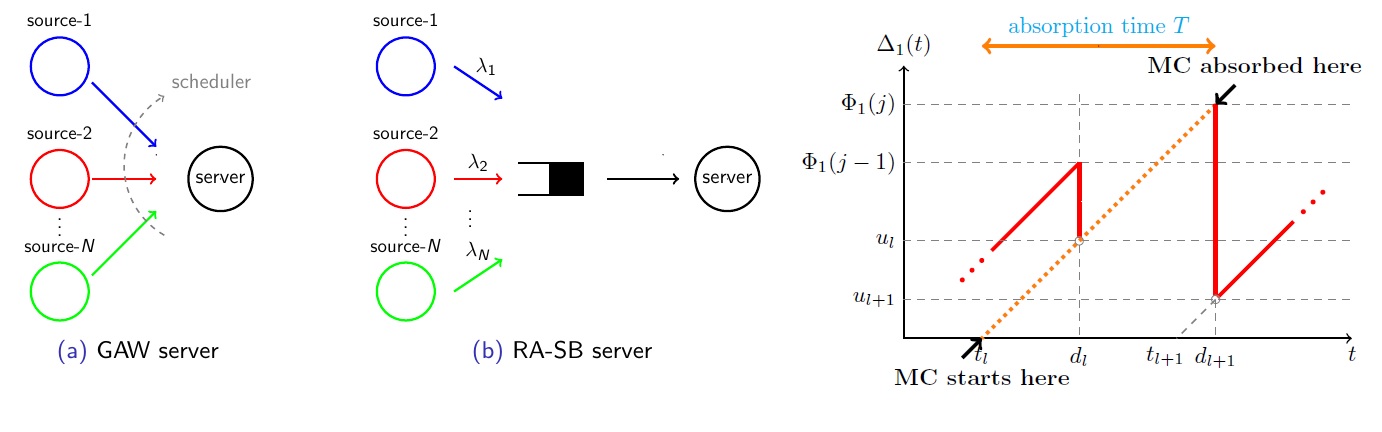
The concept of Age of Information (AoI) has been introduced for quantifying the timeliness of knowledge in networked control and monitoring systems. In this work, we study the distributions of the AoI and peak AoI (PAoI) for the Generate-At-Will (GAW) and Random Arrivals with Single Buffer (RA-SB) servers with general number of information sources. For both models, the information sources are heterogeneous, i.e., they have different i) general phase-type service time distributions, ii) priorities, and iii) packet error probabilities. To allow differentiation among the sources, the GAW server probabilistically schedules a fresh packet for one of the sources, whereas, for the RA-SB server, the buffer manager probabilistically replaces the source-n packet in the single buffer with a new packet arrival from another source-m. The exact distributions of the AoI and PAoI are obtained using the well-established theory of absorbing Continuous-Time Markov Chains. With numerical examples, we present the adverse effect of the variances of service times on AoI-induced performance metrics and also show that the RA-SB server can be tuned to outperform the previous buffer management approaches.
- A-optimality and D-optimality-based Optimal Precoding for Unknown Vector Parameter Estimation in the Presence of a Smart Eavesdropper
Erfan Mehdipour Abadi, Cagri Goken, Cuneyd Ozturk, Sinan Gezici
Poster Sunumu Ödülü:
- Federated Learning with Over-the-Air Aggregation over Time-Varying Channels
Büşra Tegin, Tolga M. Duman
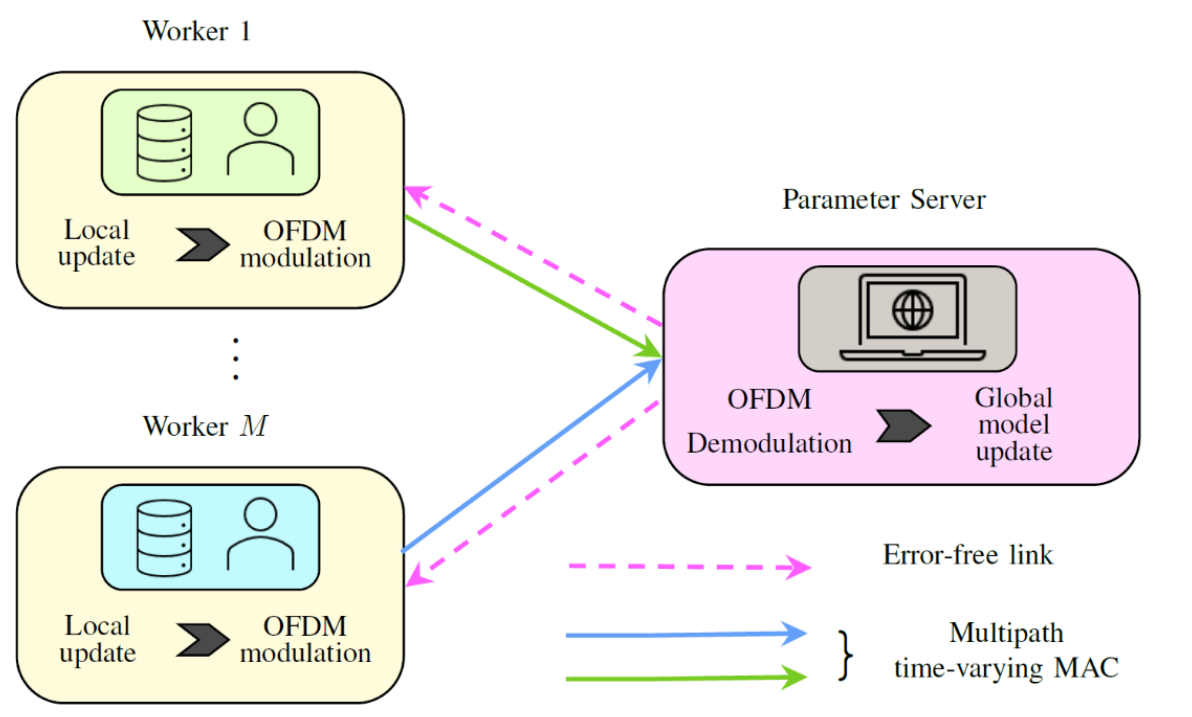
We study federated learning (FL) with over-the-air aggregation over time-varying wireless channels. Independent workers compute local gradients based on their local datasets and send them to a parameter server (PS) through a time-varying multipath fading multiple access channel via orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM). We assume that the workers do not have channel state information, hence the PS employs multiple antennas to alleviate the fading effects. Wireless channel variations result in inter-carrier interference, which has a detrimental effect on the performance of OFDM systems, especially when the channel is rapidly varying. We examine the effects of the channel time variations on the convergence of the FL with over-the-air aggregation, and show that the resulting undesired interference terms have only limited destructive effects, which do not prevent the convergence of the learning algorithm. We also validate our results via extensive simulations, which corroborate the theoretical expectations.